SMi Source lesson Osteoporosis: Skeletal Structure Exploration has the following microlearning topics
1. Skeletal Structure Exploration

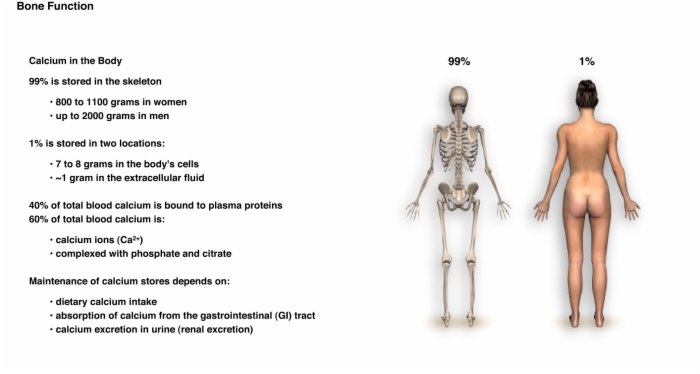
2. Calcium Homeostasis

3. Interactive Exercise: Cortical versus Trabecular Bone


4. Interactive Exercise: Blood Calcium Level


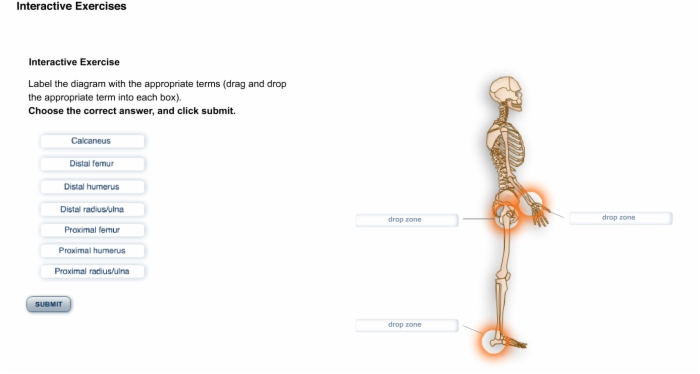
5. Interactive Exercise: Bone Identification

Lesson Osteoporosis: Skeletal Structure Exploration teaches these concepts
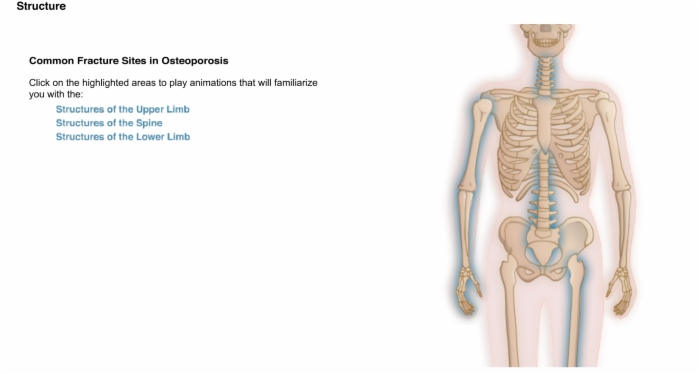
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Upper Limb
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Upper Limb: Humerus
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Upper Limb: Radius and Ulna
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Spine: Vertebral Fractures
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Spine
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Spine: Vertebrae
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Spine: Structure of the Vertebrae
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Spine: Intervertebral Discs
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Lower Limb
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Lower Limb: Femur
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites of Osteoporosis, Structures of the Lower Limb: Tibia and Fibula
Skeletal Structure Exploration, Common Fracture Sites in Osteoporosis, Structures of the Lower Limb: Foot
Lesson Osteoporosis: Skeletal Structure Exploration addresses these key points
Common sites of fracture in osteoporosis:
- Structures of the Upper Limb
- Structures of the Spine
- Structures of the Lower Limb
Structure of the upper limb:
- Arm
- Forearm
- Hand
Humerus:
- Sole bone of the arm
- Typical long bone
- Articulates with the scapula at the proximus (shoulder) and the radius and ulna at the distal end, forming the elbow
The three major regions of the bone:
- Proximus segment
- Diaphyseal segment
- Distal segment
Radius and Ulna:
- Two parallel long bones
- Form the skeleton of the forearm
- Articulate at their proximal ends with the humerus forming the elbow
- Articulate at their distal ends with the bones of the hand to form the wrist
Osteoporosis:
- Structural failure of the vertebrae
- Fractures:
- Result in compression of the spinal cord and spinal nerves as vertebrae collapse
The spine:
- Formed from vertebrae (connected series of bones)
- Supports the trunk
- Surrounds and protects the spinal cord
- Attachment point for ribs and muscles
Spinal irregularities:
- Increase risk of low back pain by straining muscles, tendons, and ligaments
- May make monitoring of conditions like osteoporosis more difficult
- Scoliosis:
- Abnormal curving of spine to the side
- Lordosis:
- Abnormally great curvature of the lower spine
Vertebrae:
- Grouped into regions and numbered
Cervical vertebrae (C1 through C7):
- Vertebrae of the neck
Thoracic vertebrae (T1 through T12):
- Next 12 vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae (L1 through L5):
- Vertebrae supporting the lower back
- Thickest individual vertebrae of the spine
Triangular sacrum (S1 through S5):
- Formed from 5 sacral vertebrae
- Fuse to form a single bone in adults
Coccyx:
- Tail bone
- Formed from 3 fused coccygeal vertebrae
Vertebrae:
- Vary in structure
- Allow different regions of the spine to perform different functions and motions
Features in common:
- Disc-shaped body or centrum at its anterior end
- Arch of bone at its posterior end
- Spinous and transverse processes are attachment points for muscles and ligaments
- Facets:
- Flattened faces of articular processes
- Cartilage-covered
- Meet to form movable joints
- Vertebral foramen:
- Space through which the spinal cord passes
Notches on the sides of the vertebrae form openings in the spine through which the spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord. From there, the spinal nerves branch and divide, and are the source of nerves for all parts of the body below the neck.
Intervertebral discs:
- Act as cushions between the vertebrae
- Lie between the bodies of successive vertebrae
- Nucleus pulposus:
- Gel-like substance at its center
- Surrounded by annulus fibrosus
Segments of the lower limb:
- Thigh
- Leg
- Foot
Femur:
- Single bone of the thigh
- Proximally articulates with the pelvic girdle
- Distally articulates with the tibia and fibula at the knee
Tibia:
- Receives weight of the body from the femur at the knee
- Transmits weight to the foot
Fibula:
- Helps to stabilize the ankle joint
Bones of the foot:
- Talus
- Calcaneus
- Navicular
- Cuboid
- Cuneiforms
- Metatarsals
- Phalanges
Lesson Osteoporosis: Skeletal Structure Exploration is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
Marieb E. Human Anatomy & Physiology 6th Ed. San Francisco Pearson; 2004. p219-245
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, NIH Publication No. 03-5161. Low Back Pain Fact Sheet, Published July 2003, updated Nov 2004.
The Merck Manual of Medical Information, 2nd Home Edition.