SMi Source lesson Biotech: Basics has the following microlearning topics
1. What is Biotechnology?


2. Biopharmaceuticals


3. Antibodies: Biotech's Most Versatile Players


4. Drug Discovery
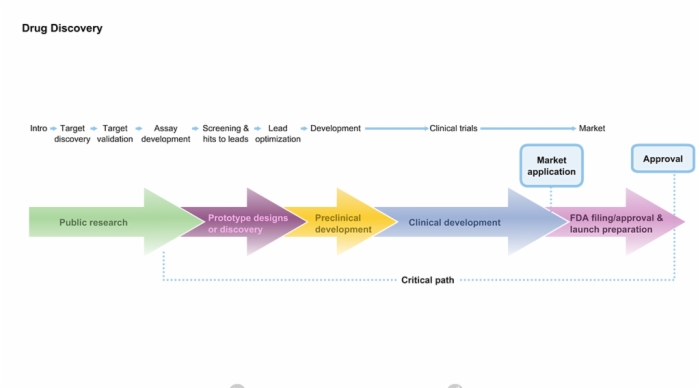

Lesson Biotech: Basics teaches these concepts
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, The History of Biotechnology
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, A Global Industry
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, The Evolution of Biotechnology
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, The Birth of Biotech
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, A Breakthrough in Treating Diabetes
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, A Paradigm for Growth Factor Signaling
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, Genetic Engineering: The Foundation of Biotech
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, Biotech's First Success Story
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, Biopharmaceuticals: Therapeutic Areas
Biotech Basics, What is Biotechnology?, Biopharmaceuticals: Sales
Lesson Biotech: Basics addresses these key points
The History of Biotechnology
- Biotechnology: the technological application of biology to produce useful products
Humans practice biotechnology to make useful products found in our everyday lives including:
- Products used to treat disease
- Penicillin
Advances in science and technology have led to the expansion of biotechnology to the use of:
- Living organisms at the cellular and molecular level
- Create more targeted and specific biopharmaceuticals
A Global Industry
- Biotech sector by market share
- Agriculture
- Bt corn is engineered to produce a bacterial toxin (Bt) which kills corn borers
- Industrial
- Biofuels or hydrogen produced from renewable biomass such as soy and switchgrass
- Healthcare
- Erythropoietin for the treatment of severe anemia
The Evolution of Biotechnology
- The discovery of the double helix structure of DNA laid the foundations for modern biotechnology
- Elucidation of the genetic code
- Cloning of DNA
- Production of monoclonal antibodies
- Recombinant proteins
- Mapping of human genome
The Birth of Biotech
- Traced back to 1972 meeting between scientists Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer
- Boyer described using enzymes to selectively cut strands of DNA and paste them back together in a different order
- Cohen described a method of introducing DNA from one bacterium into another
- They started a collaboration that led to the development of recombinant DNA technology and the scientific foundation of modern biotech
A Breakthrough in Treating Diabetes
Understanding:
- The molecular mechanisms of disease
- The biological processes that are exploited to create treatments for disease
A Paradigm for Growth Factor Signaling
- Scientists next discovered that insulin controls sugar metabolism by binding to specific receptor proteins on the surface of cells in the liver, muscle, and fat
- Binding of insulin causes the receptor to change conformation, which activates signaling cascades within the cell leading to increased glucose uptake and metabolism
Insulin gene
- Contains the information encoded in its nucleotide sequence for the production of insulin protein.
In living cells this occurs in two steps:
- DNA is transcribed into a complementary form of messenger RNA in the nucleus
- RNA message is read and translated into protein at ribosomes in the cytoplasm
- Process holds true for all organisms from bacteria to humans
Biotech's First Success Story
- Insulin was one of the first recombinant proteins to be made in a lab
- The success of modern biotech in safely treating diseases like diabetes relies upon understanding the molecular mechanisms of the disease and how to produce large quantities of active, safe recombinant proteins
Since the approval of recombinant human insulin in 1982:
- The treatment of type I diabetes has kept pace with progress in the biotech industry
- Faster acting forms of insulin
- Pens improved insulin delivery
- Devices for monitoring blood glucose levels
Biopharmaceuticals: Therapeutic Areas
- > 120 approved 1982-2012 in US, EU
- Biopharmaceuticals are part of a larger group of therapeutic products called biologics, which also include blood products, such as anti-clotting factors, and vaccines
Biopharmaceuticals: Sales
- Altogether 7 out of the top 10 drugs are projected to be biologics, with 6 of these being antibody products
- Looking further ahead still, projections for 2016 suggest that 63% of global sales of the top 20 drugs will be of biopharmaceuticals
Lesson Biotech: Basics is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
BIO website; bio.org
Biotech 2012: Innovating in the New Austerity; Burrill & Company’s 26th Annual Report of the Life Sciences Industry
Ernst & Young Annual Biotech Industry Report, 2011
ISAAA Annual Review, 2011
Leader, B, Baca, QJ, Golan, DE Nat Rev Drug Disc 7; 21-39 (2010)
Nature Medicine 18; 636 (2012)
Lesson Biotech: Basics introduces and defines these terms
EGF = Epidermal Growth Factor